Learn the difference between longitudinal and time series data
Published:
With the advancement of technology, big data can now be stored indefinitely. Keeping historical data allows analysts to understand the past and better predict the future. The analysis of these historical data is most dependent to time. Indeed, depending on the nature of the time variable, its frequency and the type of sample concerned, we can analyze these types of data in different ways: time series analysis, longitudinal data analysis, panel data analysis, etc. The proposed definitions allow the terms to be clarified and the difference to be made, and to be able to choose the best modeling for the analysis.
Introduction
Longitudinal and time series data are confusing when it comes to analysing historical data. There are no strict and formal definitions on which a wide range of data analysts agree. In the literature, we have noticed that there are very few articles on the subject. And the few articles that do mention it, skim over the definition [1].
However, given that these two types of data have temporality in common, it is necessary to distinguish between them in order to better choose the appropriate analysis methods. We have cross-read articles from three different sources with the search terms time series analysis and longitudinal data analysis in English, in order to try to provide precise definitions.
In the literature, we have noticed that there are very few articles on the subject. And the few articles that do mention it, skim over the definition [1]. We have cross-read articles from different sources with the search terms time series analysis and longitudinal data analysis , in order to try to provide precise definitions. This study also explores and compares methods for clustering analysis of panel data via multidimensional distance measures, longitudinal clustering and multidimensional sequence analysis.
This systematic review was carried out on the Google, Google Scholar and Research Gate databases, and according to the StackExchange communauty. Moreover, all references cited in the articles were explored, and a manual search was carried out.
Time series data definition
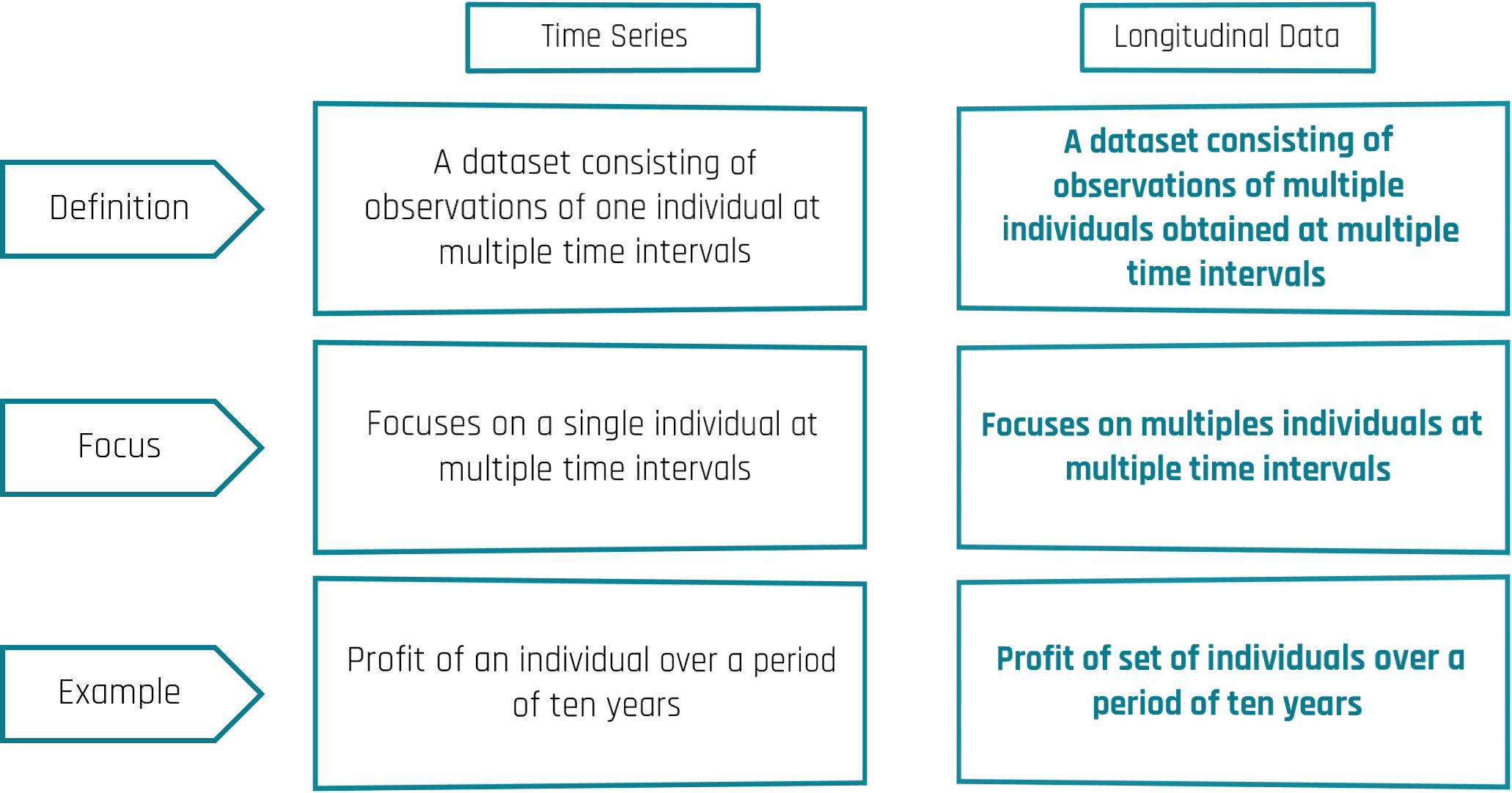
Time series data can be defined as a study unit observed at regular intervals over a very long period of time. It focuses on observations of a single individual at different times. Viewed as a dataset, think of it as one column with rows corresponding to different time points.
- Single individual and at multiple points times
Cross-Sectional data definition
Cross-Sectional data is a collection of observations for multiple subjects (study units) at single point in time.
- Multiple individuals and at the same time
Longitudinal data definition
Longitudinal data (or panel data) refers to a larger number of study units observed over a few period of time. It is usually called as Cross-sectional Time-series data as it a combination of above mentioned types, i.e., collection of observations for multiple subjects at multiple instances. Think of it as a table where rows are time points, and columns are subjects.
- Multiple individuals and at multiple points times
References
[1] S Fienberg, I Olkin, and G Casella. Springer texts in statistics. Longitudinal and Time-Series Analysis - 342p
